Treatment for shoulder pain
An overview
ÜBERSICHT
Rotator cuff injuries
A tear in the rotator cuff(rotator cuff lesion) can occur as a result of an acute injury (e.g. shoulder dislocation), but degeneration or tear formation is much more common due to chronic wear and tear or irritation (e.g. impingement syndrome). This often progresses gradually and imperceptibly until symptoms suddenly appear, often as a result of minor trauma. Prolonged pain, calcification or irritation often precede the formation of tears.
AC joint arthrosis
Signs of wear in the AC joint (acromioclavicular joint)): Cartilage wear, joint space narrowing and osteophyte formation (bone build-up) occur. AC joint arthrosis mainly occurs during prolonged physical work, in strength athletes or after a trauma such as an AC joint dislocation.
Diagnosis: The clinical examination can already very specifically identify AC joint osteoarthritis. An X-ray can reveal narrowing of the joint space and bony growths (osteophytes). Magnetic resonance imaging is only helpful to rule out other pathologies.
Therapy: Conservative treatment is always the first priority. This includes anti-inflammatory medication, but also injections of cortisone or ACP therapy. If the symptoms do not improve despite conservative measures, surgery using the keyhole technique (arthroscopy) must be considered.
Shoulder dislocation (dislocated shoulder)
A shoulder dislocation usually occurs after a violent impact with excessive external rotation and abduction of the arm. After the shoulder has been straightened, there are often hardly any complaints after a few weeks.
However, after such a traumatic event, it is important to clarify and treat the concomitant injuries (cartilage damage, tendon injuries, labral tears, etc.). It is just as important to prevent a new dislocation, 90% of which will occur again without treatment in people under 30 years of age.
The treatment plan is individualized depending on the age of the patient, the concomitant injuries and the requirements of the injured shoulder.
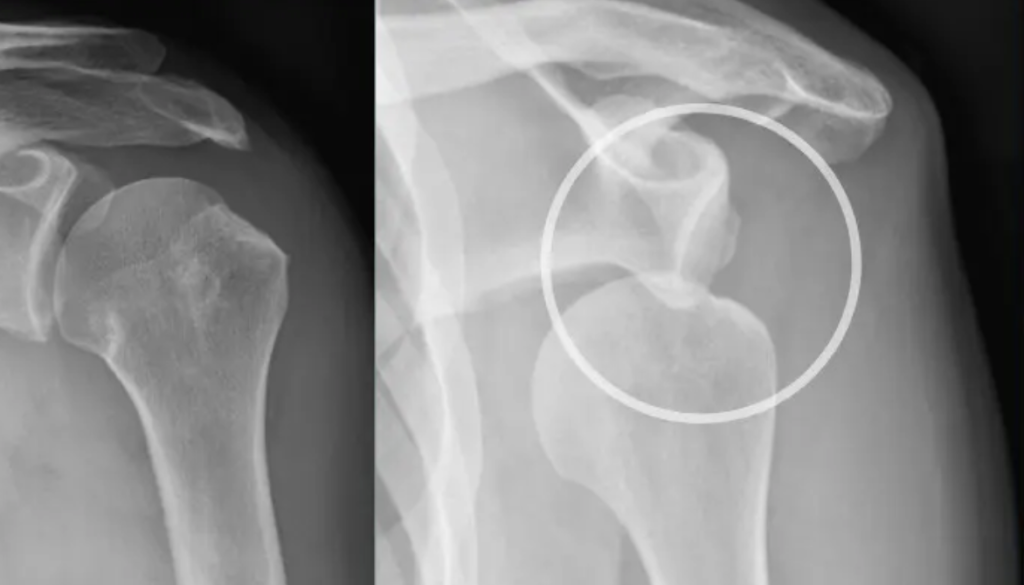
Calcified shoulder

Shoulder pain during overhead or throwing sports
In these sports, extreme external rotation in the shoulder joint with simultaneous abduction (lateral abduction) is usually the cause of the pain. The tendon insertion of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendon at the posterior edge of the glenoid cavity is crushed. In the case of prolonged stress intensities over several years, the patient benefits from increased external rotation with a simultaneous reduction in internal rotation capability. This results in overstretching of the anterior shoulder capsule and a shrunken posterior capsule. This is the full picture of the so-called GIRD syndrome (Glenohumeral Internal Rotation Deficit)

AC joint dislocations
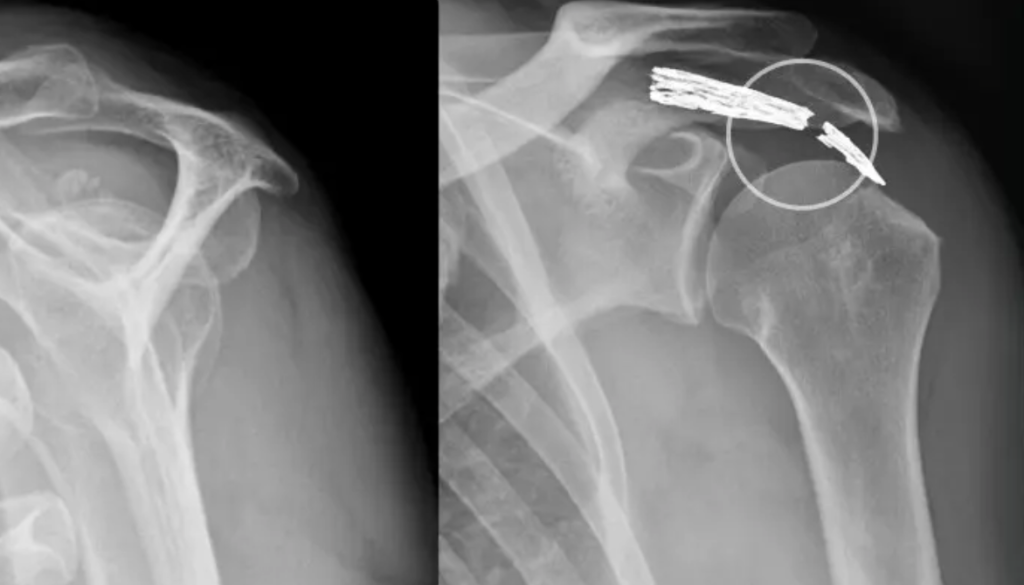
AC joint dislocation is the term used to describe injury to the ligaments that stabilize the joint between the acromion and clavicle. According to the Rockwood classification, different degrees of injury are described, which helps doctors to determine the indication for surgery. Grades I-II should be treated conservatively with rest, avoidance of weight bearing and spreading the arm over 90° for approx. 6 weeks. From grade III, surgical treatment should be considered, as otherwise permanent shoulder pain or AC joint arthrosis may develop.

Upper arm fractures (fractures)
In order to gain a clear understanding of the individual anatomy, preoperative planning is essential in arthroplasty today. In fracture treatment, too, it is particularly important for me to have a precise plan before the operation to determine the size and alignment of the implant. This is the only way to minimize the unforeseen in order to achieve an optimal result.